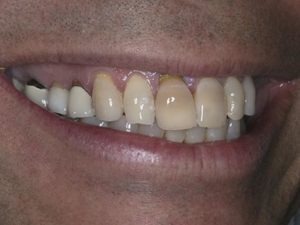
Your gums are crucial for supporting the roots and crowns of your teeth. Their soft tissues offer protection from harmful oral bacteria in plaque and extreme temperature fluctuations. They also play an active role in keeping teeth firmly in place and aligned. Therefore, gum recession, or shrinking gum lines, is an issue that must be addressed quickly. While the incidence of recession has been found to increase with age, age alone has not been determined as an actual cause of recession. Below, we’ll explore the steps you can take to help delay the onset of gum recession—or perhaps avoid it altogether.
Your Gums’ Anatomy
Teeth are supported by hard tissues (such as the jaw bone) and soft tissues (such as periodontal ligaments and gums). There are two types of exposed gum that perform different roles in the support and protection of the teeth.
- “Free gingiva” is the looser tissue which most closely surrounds the visible area of the tooth and is not directly attached to the tooth. You probably notice this area of the gums when flossing: a thread of floss can usually move up underneath this lowest area of the gums.
- “Attached gingiva” is directly above the free mucosa, and plays an important in protecting the underlying teeth roots from bacterial infection. The health and functionality of your teeth depend upon maintaining a certain level of attached gingiva.
- Just above the attached gingiva, is a darker, reddish area of gums that is not firmly connected. It is called “mucogingival tissue.” It is thinner and softer than the attached gingiva and connects the attached gingiva to the cheeks and other soft tissues in the mouth.
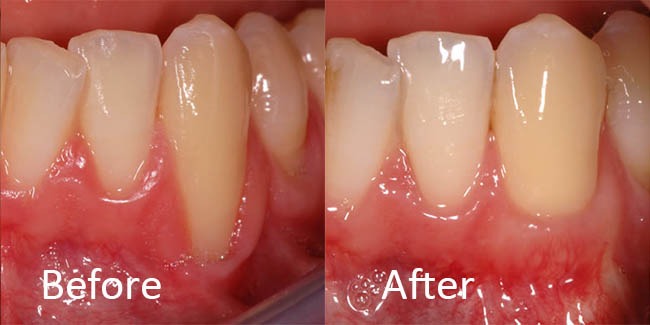
This gingival recession was caused by several things. Plaque and tartar buildup caused inflammation of the gums. There may have been some bone loss also. This patient also had braces which unfortunately pushed the root outside the boney housing. Left untreated, this tooth could be lost. This receded area was treated with scaling and root planing and a gum graft
What Gum Recession Means for You
As we age, more of our teeth surfaces become exposed. In fact, recession can even reveal the roots of your teeth. This is problematic since gums typically protect teeth at that level. Gums keep food from getting between and under teeth. If food were to stick in these spaces and not be removed, they would breed bacteria, infecting the mouth beneath the gum line. Such infection leads to gum disease. But, keeping your mouth clean during this time in life can keep gum disease from setting in. Regular brushing, flossing, and appointments with your dentist help keep your mouth free of excessive bacteria.
Understanding Gum Recession
If the attached gingiva is destroyed for some reason, it exposes the root of the tooth directly underneath. This process is called gum recession. Its impacts are huge because exposed tooth roots create a host of issues. Tooth roots do not match the hard, impenetrable enamel layers of the tooth crown; their softer, more vulnerable surface makes them an easy target for harmful oral bacteria. Therefore, tooth decay can occur quickly (and with devastating effects) on this area of the tooth. Root surface is also an area that transmits temperature sensitivity. When exposed directly to temperature fluctuations from food and drink, the roots can cause painful sensitivity for patients. As more and more gum tissue recedes, these problems only continue to grow.
When to Expect Gum Recession
No matter how healthy we are, recession is inevitable. Growing older lowers our energy level, decreasing the strength of our gums. As a result, we typically encounter receding gums as we age, but poor oral care or teeth grinding can make gums recede earlier in life. Wearing a mouth guard at night if you grind in your sleep may help keep your gums at a normal level longer. Dentists recommend using an effective toothbrush to rid your mouth of food particles. When brushing, consider less abrasive toothpastes. The less aggressive you are with your teeth preceding gum recession, the better.
The Causes of a Receding Gumline
Gum recession has two main causes: infection and trauma. One of the most common causes of gum recession is gum disease, or periodontal disease. The bacteria responsible for gum disease releases corrosive, acidic waste that causes gums to bleed and become sore and inflamed. In advanced stages of gum disease, gums slowly detach from teeth and cause loose teeth, and in extreme cases, missing teeth. Advice and treatment from a gum specialist is recommended. Normal treatment starts with a deep cleaning of your teeth and gums.
In addition, smokers or those patients who use tobacco products may also experience gum recession due to their increased chances of developing periodontitis, or advanced periodontal disease. Smoking hardens the gums and restricts blood flow which can make gums less capable of fending off oral bacteria invasion.
Believe it or not, trauma to the gum line is most often caused by a toothbrush. That’s right, vigorous tooth brushers are actually more likely than those who don’t brush their teeth at all to develop receding gums later in life. This does not mean that you should forego brushing your teeth however. That would put you at a much higher risk for gum disease and cavities, and therefore tooth loss and gum recession. What this does mean is that you should be sure to practice careful tooth brushing habits.
Protect your gums
If you want to keep your teeth clean by brushing, but also protect your gums, then follow these pointers:
- Use a soft bristled toothbrush. Some people claim their teeth just don’t feel clean unless they use medium or hard bristles. Trust your dentists when they say that soft bristles do the job just as well, and have the added benefit of protecting your gums.
- Brush in circles, not up or down or side to side.
- It is recommended to brush your teeth for at least two minutes twice a day. Flossing daily cleans the 40 percent of your teeth’s surfaces not touched by brushing.
- Pressing down too aggressively when you brush. Pushing down too hard can cut or damage the fragile gum tissue.
Another cause of trauma which can lead to gum recession include ill fitting oral appliances. If you have partial dentures, full dentures, or a dental bridge that is not fitting correctly, the appliance could create friction between it and gum tissue with every bite. Over time, this friction compounds to actually wear away healthy gum tissue and cause receding gum lines. This is why it’s imperative to seek out early treatment if your dental appliance starts feeling uncomfortable or different.
Treatment Alternatives
While grafting is the primary treatment option, gum contouring is also a frequent treatment choice.
